This example uses the Health Thermometer Profile to send thermometer information: The canonical source for this example lives at https://github.com/ARMmbed/mbed-os-example-ble/tree/master/BLE_Thermometer
Thermometer
This example uses the Health Thermometer Profile to send thermometer information:
- Sensor location: thermometer placement on the body. The default value in this application is the ear (``LOCATION_EAR``). The characteristic description shows the other possible values.
- Temperature: the initial temperature is 39.6, and it's incremented by 0.1 every half second. It resets to 39.6 when it reaches 43.0.
For more information see:
- Temperature Service: GATT profile details.
- Temperature Measurement: GATT characteristic details for temperature measurement.
- Temperature Type: GATT characteristic details for temperature type (sensor location).
Running the application
Requirements
The sample application can be seen on any BLE scanner on a smartphone. If you don't have a scanner on your phone, please install :
- nRF Master Control Panel for Android.
- LightBlue for iPhone.
Hardware requirements are in the main readme.
Building instructions
Building with mbed CLI
If you'd like to use mbed CLI to build this, then you should refer to the main readme. The instructions here relate to using the developer.mbed.org Online Compiler
In order to build this example in the mbed Online Compiler, first import the example using the ‘Import’ button on the right hand side.
Next, select a platform to build for. This must either be a platform that supports BLE, for example the NRF51-DK, or one of the following:
List of platforms supporting Bluetooth Low Energy
Or you must also add a piece of hardware and the supporting library that includes a Bluetooth Low Energy driver for that hardware, for example the K64F or NUCLEO_F401RE with the X-NUCLEO-IDB05A1
List of components supporting Bluetooth Low Energy.
Once you have selected your platform, compile the example and drag and drop the resulting binary onto your board.
For general instructions on using the mbed Online Compiler, please see the mbed Handbook
Checking for success
Note: Screens captures depicted below show what is expected from this example if the scanner used is *nRF Master Control Panel* version 4.0.5. If you encounter any difficulties consider trying another scanner or another version of nRF Master Control Panel. Alternative scanners may require reference to their manuals.
- Build the application and install it on your board as explained in the building instructions.
- Open the BLE scanner on your phone.
- Start a scan.
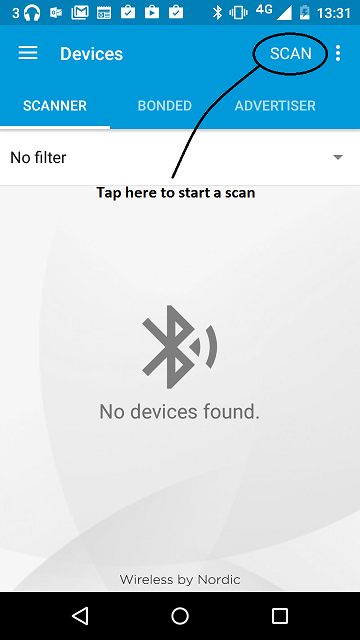
figure 1 How to start scan using nRF Master Control Panel 4.0.5
- Find your device; it should be named *Therm*.
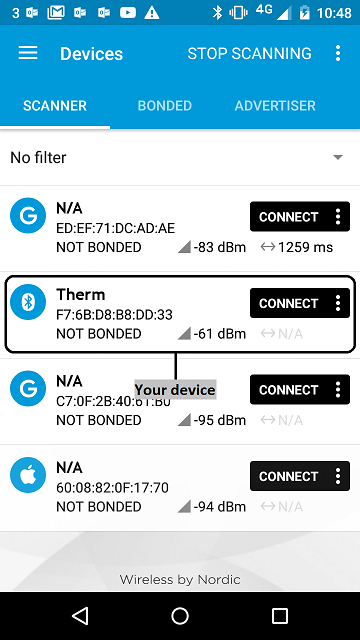
figure 2 Scan results using nRF Master Control Panel 4.0.5
- Establish a connection with your device.
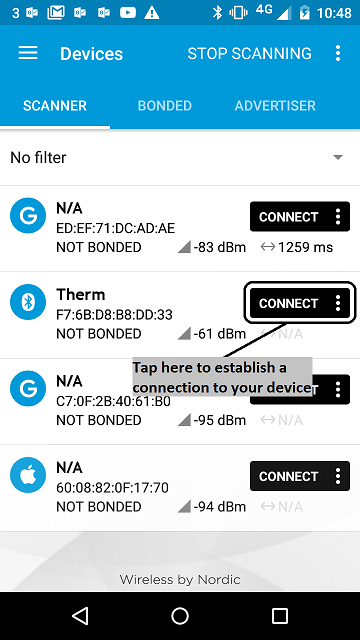
figure 3 How to establish a connection using Master Control Panel 4.0.5
- Discover the services and the characteristics on the device. The *Health Thermometer* service has the UUID `0x1809` and includes the *Temperature Measurement* characteristic which has the UUID `0x2A1C`.
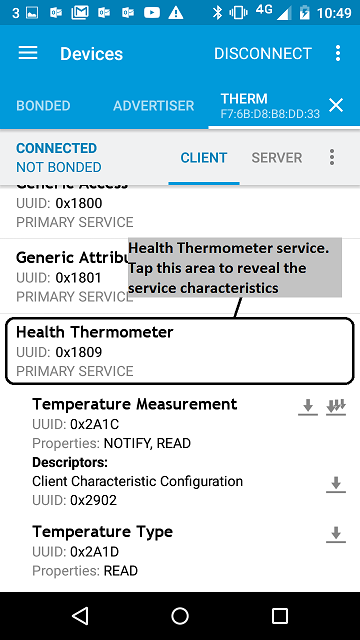
figure 4 Representation of the Thermometer service using Master Control Panel 4.0.5
- Register for the notifications sent by the *Temperature Measurement* characteristic.
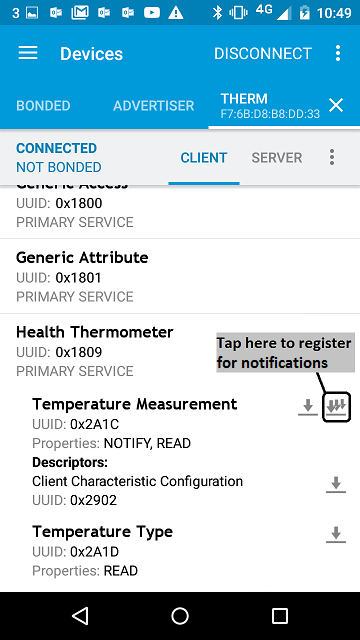
figure 5 How to register to notifications using Master Control Panel 4.0.5
- You should see the temperature value change every half second. It begins at 39.6, goes up to 43.0 (in steps of 0.1), resets to 39.6 and so on.
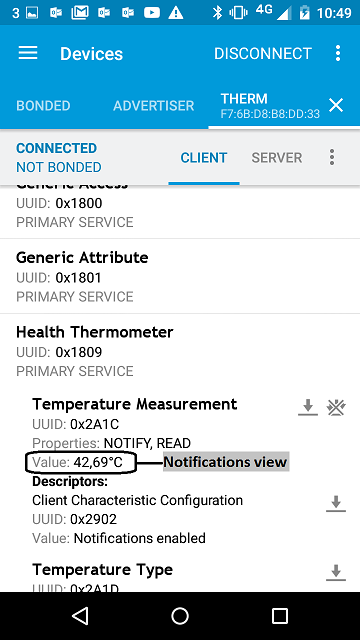
figure 6 Notifications view using Master Control Panel 4.0.5
Revisions of source/main.cpp
| Revision | Date | Message | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11:4e356c89ad66 | 2016-10-24 | Merge pull request #32 from ARMmbed/oob | File Diff Annotate |
| 2:cc8349878a7d | 2016-07-28 | Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/ARMmbed/mbed-os-example-ble | File Diff Annotate |
| 1:0802a5f8c9d3 | 2016-07-28 | Sync with mbed-os-5.1.0-rc3 | File Diff Annotate |
| 0:a27dfda81620 | 2016-07-26 | Update example at tag mbed-os-5.0.1-rc1 | File Diff Annotate |
 mbed-os-examples
mbed-os-examples