You are viewing an older revision! See the latest version
CMSIS DAP MDK
Background¶
Since its launch the mbed platform has always avoided the temptation to offer a debug facility, instead opting for LEDs and and serial port printf. In the last 12 months it has become possible to export mbed projects to offline tool chains such as MDK, Code Red and GCC, but the proprietary nature of their interfaces prevented a clean solution for debug.
ARMs newly announced CMSIS-DAP debug interface consists of and abstraction of the Cortex Debug Access Port (DAP) command set over a driver-less USB HID connection. This provides a USB connection to the DAP that major tool vendors have started to support. It even provides the flexibility for users to write their own debugger, or debug script using the USB bindings in languages like Python.
mbed Architecture¶
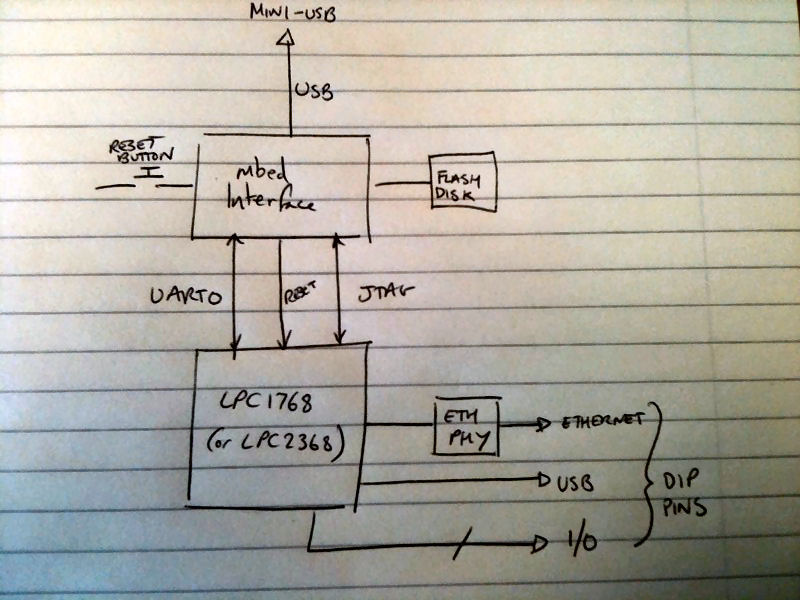
The mbed microcontroller includes the mbed onboard interface which provides a drag and drop programming interface and a virtual serial port, and accesses the target MCU usign cortex Serial Wire Debug (SWD) as any debug probe would. With the advent of CMSIS-DAP, the mbed onboard interface has been upgraded to include an USB HID end point . This enables mbed users to connect to their mbed microcontroller from an offline tool, such as Keil MDK, to perform operations such as image downloading, break points and source level debug.
This picture should help clarify how the mbed microcontroller is built
Current limitations¶
For the purpose of this trial, it will not be possible to debug applications that use semi-hosting calls to the mbed interface. Examples of these calls are :
- Accessing the local file system
- Ethernet applications where the MAC address is provided by the interface (default)
- Accessing the power down functions of the interface
This is because the MDK does not currently support the use of semihosting calls.
Getting started¶
To try the mbed CMSIS-DAP upgrade you will need :
- The firmware that supports CMSIS-DAP for your target:
- LPC1768 - LPC11U24
- FRDM-KL25Z: mbed_if_v2.0_frdm_kl25z.s19
- An offline tool that support CMSIS-DAP - Keil MDK v4.60 for example
- An example project you wish to debug!
1. Upgrading your board¶
a - LPC1768 - LPC11U24¶
To upgrade the mbed Microcontroller, simply download the file below to your mbed microcontroller, unplug it, and plug it back in again.
After a few seconds after you plug the mbed microcontroller back in, the USB disk will appear and the upgrade file will have been deleted.
Restoring your mbed
Should you wish to revert your mbed back to its original state without CMSIS-DAP, simply copy on the latest firmware file, and power cycle the mbed. This will reflash the interface back to its original state.
b - FRDM-KL25Z¶
Follow the instructions on the following page to upgrade the firmware on your FRDM-KL25Z:
c - Results¶
There will now be three mbed USB devices in device manager :
- USB disk
- mbed Serial port
- mbed CMSIS-DAP

Driver issue
If the serial is not recognised by the host:
- go into the device manager
- right click on "mbed composite"
- uninstall the driver
- then disconnect/connect your mbed
- install the serial driver
2. Install an offline tool¶
The recommended offline tool is Keil MDK v4.60. Follow the links and instructions to set up the evaluation copy.
3. Export a project¶
µVision is one of the external offline toolchains supported by the mbed platform.
For a complete overview of the "export" feature, please refer to our general: Exporting to offline toolchains.
To export your mbed program for use in uVision, right-click the program in your program workspace. From the dialog, you can select the "Export To" as "Keil uVision4", and the target microcontroller you wish to export for.
When you choose export, a zip file containing all the files you need for uVision will be generated. Unzip it and open the uVision project file (In this case, "project.uvproj"):

4. Compile, download, debug!¶
Once you have unzipped and opened the ".uvproj" file, your project should appear in the uVision IDE much in the same way it appeared in the online compiler. You can browse the project files by navigating in the left panel, and the code will appear in the main panel.
4.1 Compile¶
When the project has successfully compiled, "fromelf" will automatically run, to extract a binary file. This could be drag and dropped onto the mbed flash disk.

4.2 Download¶
With the CMSIS-DAP upgrade, clicking the download button within uVision will send the binary directly to the flash of the MCU

4.3 Debug¶
Add break points (1) by clicking on the line of code you wish to stop at, and use the "run" button (2) to execute the program until the break point it hit.

The tools enable you to step in various ways over/into/out of
Use the tool bar to add registers, memory, call stack, symbol and watch windows. This gives visibility on the system status when a breakpoint is reached.

5. Conclusion¶
A simple firmware upgrade of your board enables the on-board programming interface to communicate with debugging tools over the new CMSIS-DAP protocol. Over time we hope this will mean mbed will become interoperable with a wide range of offline tools, proving professional debug capabilities when they are needed.