Eddystone beacons broadcast a small amount of information, like URLs, to nearby BLE devices. The canonical source for this example lives at https://github.com/ARMmbed/mbed-os-example-ble/tree/master/BLE_EddystoneService
Eddystone beacons broadcast a small amount of information, like URLs, to nearby BLE devices.
The Eddystone Beacon sample application runs in two stages:
- On startup, the Configuration Service (which allows modification of the beacon runs for a user-defined period (default - 30 seconds).
- When the Configuration Service period ends, the Eddystone Service broadcasts advertisement packets.
Running the application
Requirements
You should install the *Physical Web* application on your phone:
Note: It is also possible to use a regular scanner to interract with your Eddystone beacon but it requires knowledge about BLE and Eddystone beacon specification out of the scope of this document.
Hardware requirements are in the main readme.
Building instructions
Building with mbed CLI
If you'd like to use mbed CLI to build this, then you should refer to the main readme. The instructions here relate to using the developer.mbed.org Online Compiler
In order to build this example in the mbed Online Compiler, first import the example using the ‘Import’ button on the right hand side.
Next, select a platform to build for. This must either be a platform that supports BLE, for example the NRF51-DK, or one of the following:
List of platforms supporting Bluetooth Low Energy
Or you must also add a piece of hardware and the supporting library that includes a Bluetooth Low Energy driver for that hardware, for example the K64F or NUCLEO_F401RE with the X-NUCLEO-IDB05A1
List of components supporting Bluetooth Low Energy.
Once you have selected your platform, compile the example and drag and drop the resulting binary onto your board.
For general instructions on using the mbed Online Compiler, please see the mbed Handbook
Working with nRF51-based 16K targets
Because of memory constraints, you can't use the SoftDevice 130 (S130) to build for nRF51-based 16K targets. If you are using these targets, then before building:
- Open the ``config.json`` file in this sample.
- Change ``soft device`` to ``S110``.
- Save.
You can now build for nRF51-based 16K targets.
Setting up the beacon
By default, the beacon directs to the url ``http://mbed.org``. You can change this to your own URL in two ways:
- Manually edit the code in ``main.cpp`` in your copy of the sample.
- Build and run the application's default code as explained in the building instructions. When the beacon starts up, the Configuration Service runs for 30 seconds (this is the default value; you can change it in ``main.cpp``). While the Configuration Service runs, you can use a BLE scanner on your phone to edit the values the service presents.
Checking for success
- Build the application and install it on your board as explained in the building instructions.
- Open the *Physical Web* application on your phone. It will start to search for nearby beacons.
figure 1 Start of the *Physical Web* application version 0.1.856 on Android
- When the beacon starts up, the Configuration Service runs for 30 seconds. During this time it is possible to change the URL advertised by the beacon. It is also important to note that during these 30 seconds, your device will not advertise any URL.
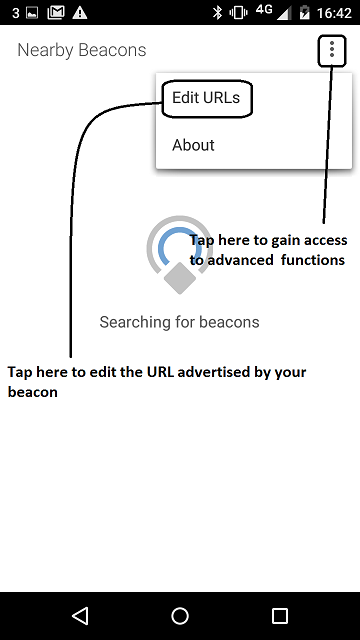
figure 2 How to open the beacon configuration view using the *Physical Web* application version 0.1.856 on Android
- Edit the URL advertised by your beacon.
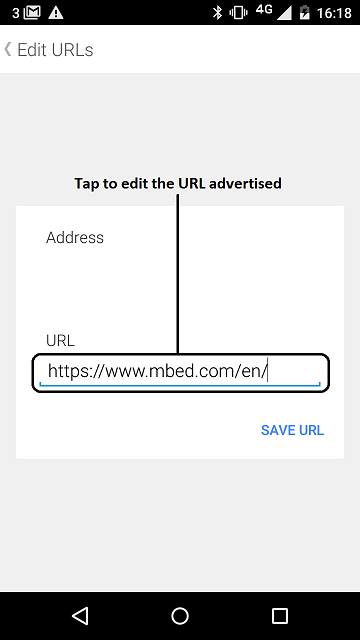
figure 3 How to edit the URL advertised by your beacon using the *Physical Web* application version 0.1.856 on Android
- Save the URL which will be advertised by your beacon.
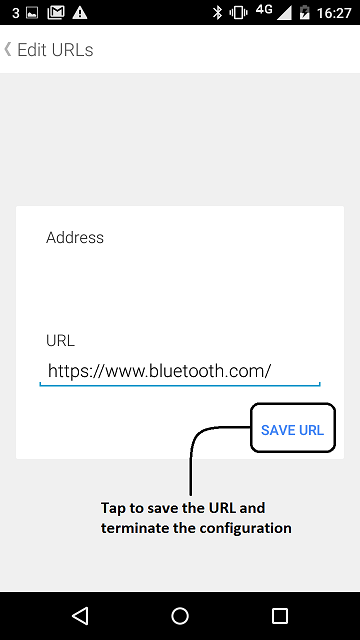
figure 4 How to save your beacon configuration and start advertising URL using the *Physical Web* application version 0.1.856 on Android.
- Find your device; it should advertise the URL you have set.
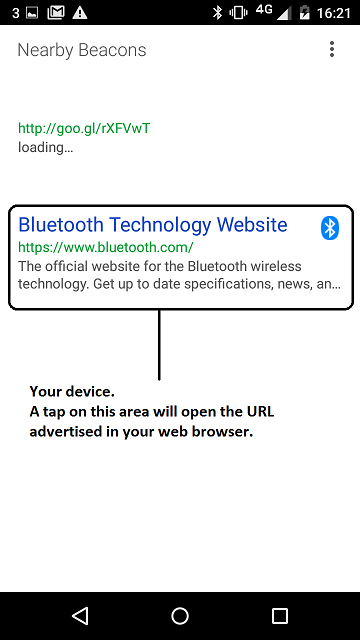
figure 5 Display of URL advertised by your beacon using the *Physical Web* application version 0.1.856 on Android.
Note: You can use the Eddystone Observer sample instead of a phone application.
 mbed-os-examples
mbed-os-examples