You are viewing an older revision! See the latest version
LSM303D
The LSM303D is a system-in-package featuring a 3D digital linear acceleration sensor and a 3D digital magnetic sensor. The LSM303D has linear acceleration full scales of ±2g / ±4g / ±6g / ±8g / ±16g and a magnetic field full scale of ±2 / ±4 / ±8 / ±12 gauss. The LSM303D includes an I2C serial bus interface that supports standard and fast mode (100 kHz and 400 kHz) and SPI serial standard interface. This LSM303 carrier board includes a 3.3 V voltage regulator and integrated level shifters that allows operation from 2.5 to 5.5 V, and the 0.1″ pin spacing makes it easy to use with standard solderless breadboards.
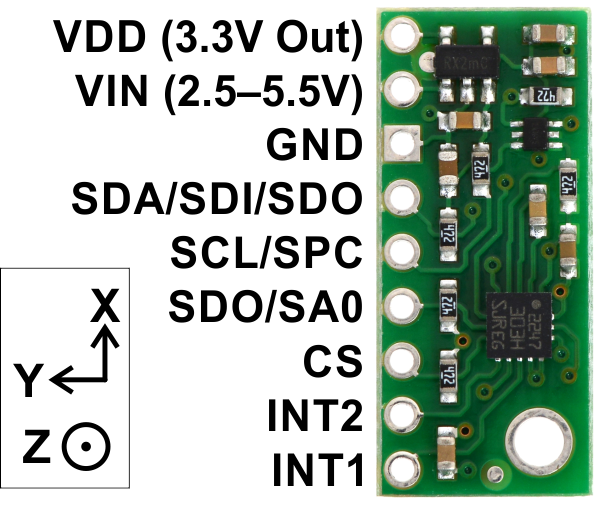
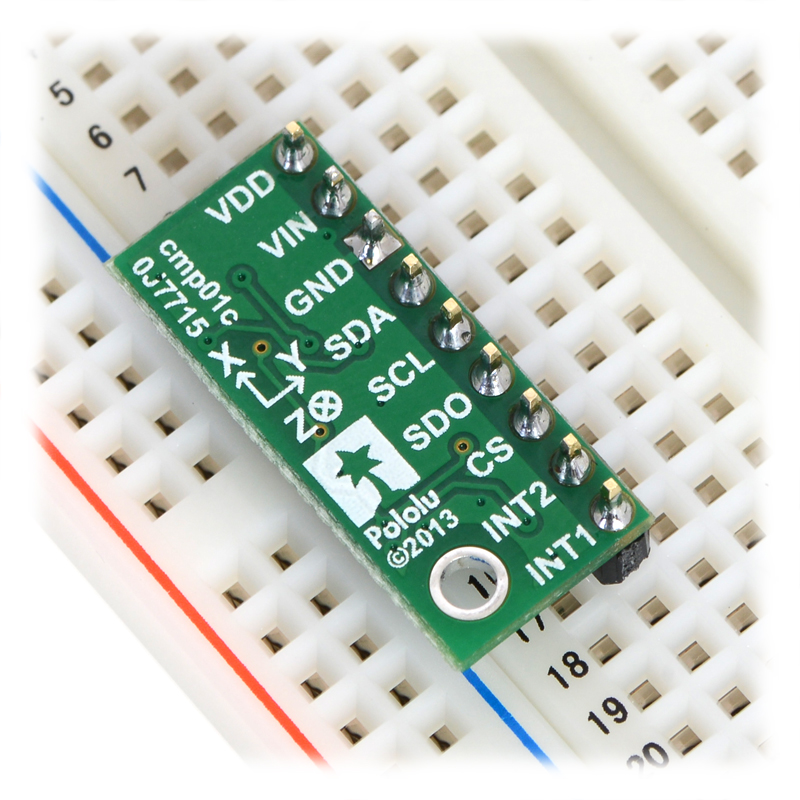
This notebook page will provide information to set up LSM303D to connect with mbed NXP LPC1768 using SPI communication.
Setup¶

SPI mode Pinout¶
| LSM303D pin | mbed pin for SPI 4-wire mode | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VDD | ||
| VIN | VOUT | 3.3V regulated out |
| GND | GND | |
| SDA | p5 | mosi |
| SCL | p7 | sck |
| SDO | p6 | miso |
| CS | p8 | chip select |
| INT2 | ||
| INT1 |
Magnetic Field Cancellation¶
The LSM303D is often used to calculate pitch, heading, and roll, using the earth's magnetic field to calculate the heading. Alternatively, the LSM303D can be used to track the location of a magnet relative to the chip. To accurately measure the magnet's location, users must cancel out the earth's magnetic field using rotational matrices to calculate the chip's orientation.
Rotational matrices are square matrices that project one directional vector onto another when multiplying the rotation matrix (R) by the original vector (a). In the LSM303D library, the rotational matrix is calculated using the method found on the website Stack Exchange's math forum Link].
As seen in the data below, the magnetic field cancellation implementation successfully reduces the magnetic field's strength as the chip is tilted at various angles.
Where the implementation fails is when the chip is simply rotated in the same horizontal frame. In this instance, the accelerometer is unable to capture the rotation of the chip, resulting in incorrect magnetic field readings.
LSM303D library¶
Import libraryLSM303D
This is the device library for LSM303D to interface with mbed. This code has been tested on mbed NXP LPC1768.
LSM303D library Hello World¶
main.cpp
#include "mbed.h"
#include "LSM303D.h"
DigitalOut myled(LED1);
LSM303D lsm303d_1(p5, p6, p7, p8);
static int magx,magy,magz,accx,accy,accz;
static LSM303D::raw_data accxx,accyy,acczz,magxx,magyy,magzz;
static LSM303D::vector<LSM303D::raw_data> a,m;
int main() {
if(lsm303d_1.initialize()==0)
{
printf("Initialization failed\n");
}
while(1) {
magx= lsm303d_1.mag(LSM303D::X_AXIS);
magy= lsm303d_1.mag(LSM303D::Y_AXIS);
magz= lsm303d_1.mag(LSM303D::Z_AXIS);
lsm303d_1.mag(LSM303D::X_AXIS,&magxx);
lsm303d_1.mag(LSM303D::Y_AXIS,&magyy);
lsm303d_1.mag(LSM303D::Z_AXIS,&magzz);
m=lsm303d_1.mag();
accx= lsm303d_1.acc(LSM303D::X_AXIS);
accy= lsm303d_1.acc(LSM303D::Y_AXIS);
accz= lsm303d_1.acc(LSM303D::Z_AXIS);
lsm303d_1.acc(LSM303D::X_AXIS,&accxx);
lsm303d_1.acc(LSM303D::Y_AXIS,&accyy);
lsm303d_1.acc(LSM303D::Z_AXIS,&acczz);
a=lsm303d_1.acc();
printf("mag x: %d\n\rmag y: %d\n\rmag z: %d\n\n\r",magx,magy,magz);
printf("mag x: %d\n\rmag y: %d\n\rmag z: %d\n\n\r",magxx.raw,magyy.raw,magzz.raw);
printf("mag x: %d\n\rmag y: %d\n\rmag z: %d\n\n\r",m.x.raw,m.y.raw,m.z.raw);
printf("acc x: %d\n\racc y: %d\n\racc z: %d\n\n\r",accx,accy,accz);
printf("acc x: %d\n\racc y: %d\n\racc z: %d\n\n\r",accxx.raw,accyy.raw,acczz.raw);
printf("acc x: %d\n\racc y: %d\n\racc z: %d\n\n\r",a.x.raw,a.y.raw,a.z.raw);
myled = 1;
wait(1);
myled = 0;
wait(1);
}
}
Console output¶

