USB Speaker
USBAudio Class
The USB speaker uses USBAudio class which enables mbed work as an external sound card. The audio amplifier and surface transducer make it possible to play music on any surface.
We use a Mini-USB breakout board from Sparkfun for this prototype
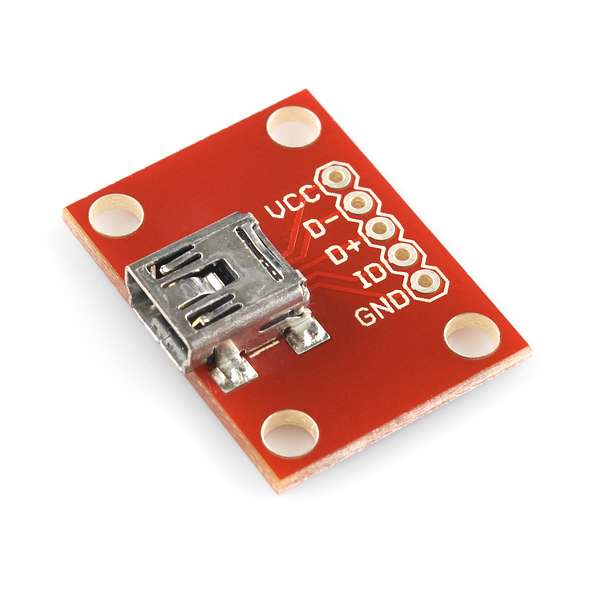
The USB connector is connected to the following pins of mbed:
| mbed | USB connecto |
|---|---|
| p31 | D+ |
| p32 | D- |
| VIN | VCC |
| GND | GND |
Sample Code for USBAudio Class
Import programUSBAUDIO_speaker
USBAudio speaker example
Turn it into a speaker
The above example code enables the mbed receive and play audio packets from your computer, but the output power of the mbed IO pin to too weak to drive a speaker directly.
A efficient class-D audio amplifier is used to boost the output of the mbed and drive the transducer. To eliminate DC component of the output, a electrolytic capacitor is used. The capacitor used in this prototype is audio-purpose capacitor from ELNA.


Two types of surface transducer can be used in this prototype. The one on the right has higher power, but be sure to limit the volume to protect the circuit.


Here is the wiring of the amplifier:
| mbed | Capacitor | Amplifier | Speaker |
|---|---|---|---|
| p18 | + | ||
| - | IN+ | ||
| GND | IN- | ||
| VIN | PWR+ | ||
| GND | PWR- | ||
| OUT+ | + | ||
| OUT- | - |
Also, a 3.5mm headphone jack is supported:
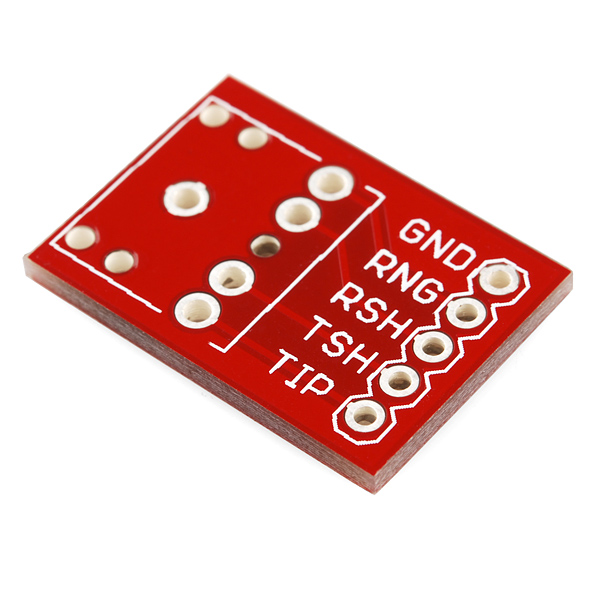
| mbed | Capacito | Headphone Jack |
|---|---|---|
| - | TIP | |
| - | RNG | |
| GND | GND |
Control Volume Using Digital Potentiometer
To make the mbed "turn the knob", a digital potentiometer is used to control the volume. The one used in this prototype is AD5206, a 6-channel, 256-position digital potentiometer. It has three terminal resistances we can choose, 10K ohm version is used in this demo.


AD5206 has 3-wire SPI-compatible serial data input, the wiring is shown in the table below:
| mbed | AD5206 |
|---|---|
| VIN | VDD |
| GND | VSS |
| GND | GND |
| p5 | SDI |
| p7 | CLK |
| p8 | CS' |
Demo Code for AD5206 Potentiometer
/*
AD5206 Test code
This program sweeps resistance output of channel 0
from 0-255 (lowest to highest value)
Connection:
| mbed | AD5206 |
| VIN | VDD |
| GND | VSS |
| GND | GND |
| p5 | SDI |
| p7 | CLK |
| p8 | CS' |
Qiuyang Tao 10/17/2015
*/
#include "mbed.h"
#include <AD5206.h>
AD5206 digipot(p5, p6, p7,p8);//MOSI, MISO, CLK, CS'
int val;
int main() {
while(1) {
digipot.write_AD5206(0,val);
val=val+1;
if (val==255){val=0;}
wait(0.1);
}
}
Here is the library for the digital potentiometer:
Import libraryAD5206
Library for AD5206 digital potentiometer from Analog Devices
Two push buttons are connected to the mbed which makes it easier to control the volume.

More details on how to push buttons can be found: https://developer.mbed.org/handbook/DigitalIn
USB Speaker with Digital Volume Control
main.cpp
// USBAudio speaker example
#include "mbed.h"
#include "USBAudio.h"
#include "AD5206.h"
AD5206 digipot(p5, p6, p7,p8);
int val=150;
DigitalOut led1(LED1);
DigitalOut led2(LED2);
DigitalIn but1(p22);
DigitalIn but2(p21);
// frequency: 48 kHz
#define FREQ 48000
// 1 channel: mono
#define NB_CHA 1
// length of an audio packet: each ms, we receive 48 * 16bits ->48 * 2 bytes. as there is one channel, the length will be 48 * 2 * 1
#define AUDIO_LENGTH_PACKET 48 * 2 * 1
// USBAudio (we just use audio packets received, we don't send audio packets to the computer in this example)
USBAudio audio(FREQ, NB_CHA, 8000, 1, 0x7180, 0x7500);
// speaker connected to the AnalogOut output. The audio stream received over USb will be sent to the speaker
AnalogOut speaker(p18);
// ticker to send data to the speaker at the good frequency
Ticker tic;
Ticker tic2;
// buffer where will be store one audio packet (LENGTH_AUDIO_PACKET/2 because we are storing int16 and not uint8)
int16_t buf[AUDIO_LENGTH_PACKET/2];
// show if an audio packet is available
volatile bool available = false;
// index of the value which will be send to the speaker
int index_buf = 0;
// previous value sent to the speaker
uint16_t p_val = 0;
// function executed each 1/FREQ s
void tic_handler() {
float speaker_value;
if (available) {
//convert 2 bytes in float
speaker_value = (float)(buf[index_buf]);
// speaker_value between 0 and 65535
speaker_value += 32768.0;
// adjust according to current volume
speaker_value *= audio.getVolume();
// as two bytes has been read, we move the index of two bytes
index_buf++;
// if we have read all the buffer, no more data available
if (index_buf == AUDIO_LENGTH_PACKET/2) {
index_buf = 0;
available = false;
}
} else {
speaker_value = p_val;
}
p_val = speaker_value;
// send value to the speaker
speaker.write_u16((uint16_t)speaker_value);
}
void tic_handler2() {
led1=0;
led2=0;
if (!but1){led1=1;val+=20;}
if (!but2){led2=1;val-=20;}
digipot.write_AD5206(0,val);
if (val>255){val=255;}
if (val<0) {val=0;}
}
int main() {
// attach a function executed each 1/FREQ s
tic.attach_us(tic_handler, 1000000.0/(float)FREQ);
tic2.attach(tic_handler2, 0.2);
while (1) {
// read an audio packet
audio.read((uint8_t *)buf);
available = true;
}
}
Import programUSB_speaker
USB Speak with Digital Volume Control
Please log in to post comments.
